Bigger Wafer
Bigger wafer, higher power of the solar cell and solar panel. In silicon solar PV industry wafer size has increased from M2, M4, G1, M6 to M10 and M12(G12).
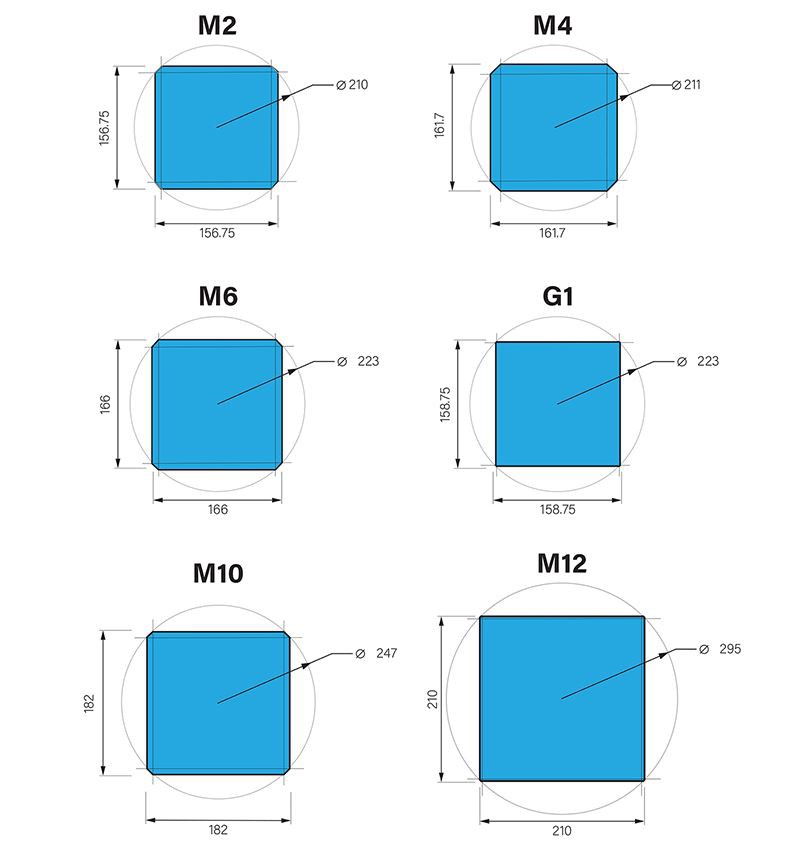
Before 2010, monocrystalline silicon wafers were dominated by 125mm x 125mm width (165mm silicon ingot diameter) and only a small number at 156mm x 156mm (200mm silicon ingot diameter).
After 2010, 156mm x 156mm wafers increasingly became the popular choice (lower cost per-watt) for p-Type monocrystalline and multicrystalline wafer sizes. Then the upheaval came to 158.75 mm wafer sizes and M6 wafers with 166mm.
Up to now, wafer sizes of 182 mm (M10) and 210 mm (M12) have arrived on the market.
Multi bus-bar (MBB)

Multi bus-bar (MBB) means that a solar cell is equipped with 9 to 18 busbars instead of 4, 5 or 6. This means the modules provide a higher power output and a higher reliability:
~2 % – 2,5 % power increase (in % range because cell eff. and types are different)
Shorter transportation path for current
High reflectance wire design with less shading
Mechanical load performance increased
Risk of micro crack decreased
Half- Cut Technology (Half-cell technology)
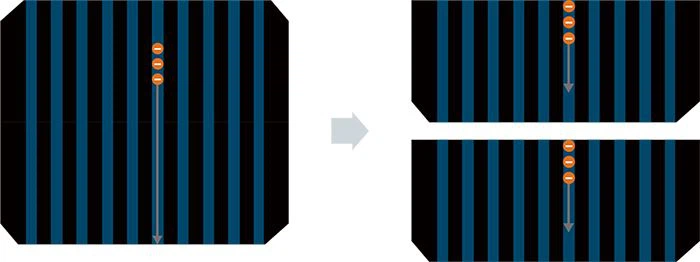
Half-cut technology features with solar cells that are cut in half, which improves the module’s performance and durability. Standard 60 and 72-cell solar modules will consist of 120 and 144 half-cut cells, respectively.
When solar cells are halved, their current is also halved, so resistive losses are lowered and the cells can produce a little more power. Smaller cells experience reduced mechanical stresses, so there is a decreased opportunity for cracking. Half-cell modules have higher output ratings and are more reliable than traditional panels.

















